Recently, a new paper “Response and Adaptation of Agriculture to Climate Change: Evidence from China” co-written by Chen Shuai and Gong binlei, two researchers of China Academy for Rural Development, Zhejiang University (ZJU), was published online in Journal of Development Economics (JDE), a top journal in development economics.

Refer to the original paper:
CHEN, Shuai, and GONG, Binlei*, 2020, Response and Adaptation of Agriculture to Climate Change: Evidence from China, Journal of Development Economics, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdeveco.2020.102557.
【Introduction】
Mitigation and adaptation are two important tools for reducing the risks of climate change. In terms of mitigation, many international climate negotiations and agreements have been made to reduce and curb global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. In terms of adaptation, however, operational policies need to be established to reduce vulnerability to climate change.

Figure 1 Impact mechanism of climate change on agricultural land output value
This paper aims to identify the mechanism of how climate change affects agriculture through various channels and the mechanism of longer-run adaptation. Using a county-panel dataset spanning the past 35 years, it evaluates the impact of global warming on agricultural total factor productivity (TFP) as well as the impacts on agricultural inputs and outputs in China. Results show that, in the short run, extreme heat has negative effects on China’s agricultural TFP and input utilization, which results in a more negative effect on agricultural output measured by yield (see Figure 1). However, longer-run adaptation has offset 37.9% of the short-run effects of extreme heat exposure on TFP (see Figure 2 and 3), while climate adaptation mitigates agricultural output loss to a greater extent due to more flexible adjustment in labor, fertilizer, and machines in the long run (Figure 3). Despite the detected climate adaptation, projections of impacts under future climate change scenarios still imply a substantial loss in China’s agriculture (Figure 4).
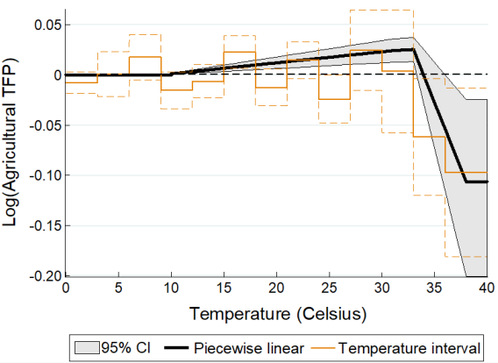
Figure 2 Effect of extreme heat exposure on agricultural TFP
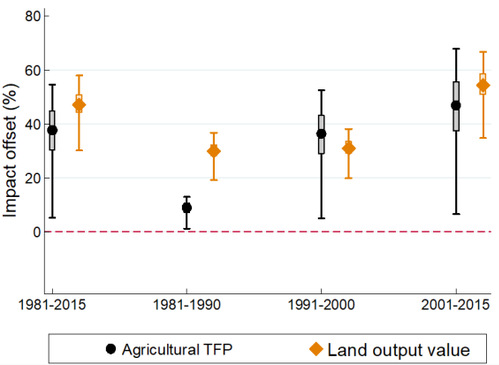
Figure 3 Human adaptation behavior offsets the short-term effects of climate change

Figure 4 Predictions of impacts of future climate change on agricultural TFP
This paper contributes to the existing literature in three major aspects. First, both yield and total factor productivity are adopted to estimate the impact of climate change on agriculture, where the latter is a better measure of agriculture productivity, but understudied in climate change literature. Second, to the authors’ best knowledge, this is the first article that identifies not only the mechanism by which climate change affects yield through its impact on TFP and input utilization, but also the mechanism of the adaptation behaviors. Third, the paper provides some of the earliest empirical evidence of nonlinear temperature effects and significant adaptation behaviors on agriculture in China based on a long study period of 35 years and a specific spatial pattern at the county level.
【Author Intro】

Chen Shuai (https://person.zju.edu.cn/shuaichen)
Receiving his PhD degree from Peking University, he now serves as an associate professor, researcher and doctoral supervisor of Zhejiang University, and teaches in the School of Public Affairs and China Academy for Rural Development. His research focuses on agricultural economics as well as resource and environmental economics, concerning issues such as climate change and socio-economic impacts of agriculture and air pollution in China. His academic papers have been published in journals such as Journal of Development Economics, Journal of the Association of Environmental and Resource Economics, Journal of Economic Geography, Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, etc.

Gong binlei (https://person.zju.edu.cn/gbl)
As an associate professor, researcher and doctoral supervisor of Zhejiang University, he also teaches in the School of Public Affairs and China Academy for Rural Development, Zhejiang University. His research focuses on development economics, concerning technical progress, productivity and growth accounting of agriculture and energy industries. His papers have been published in Journal of Development Economics, American Journal of Agricultural Economics, Energy Journal, etc.
【AcademyIntro】
China Academy for Rural Development (Carter) of Zhejiang University attaches great importance to the introduction and education of young talents. The introduction and cultivation of young talents provide a solid guarantee for the sustainable development and prosperity of agricultural economics in Zhejiang University. In recent years, researchers of this academy have published a lot of papers in international journals such as Journal of Development Economics, American Journal of Agricultural Economics, Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, and Journal of the Association of Environmental and Resource Economics, greatly enhancing the academic influence of the discipline at home and abroad.


